Healthcare technology, and specifically mobile health is booming, especially after the recent pandemic fueling the development of healthcare applications.
Growth in coverage of mobile cellular networks, increasing chronic conditions, and growing availability of patient education technology in developed and emerging economies alike have churned out better opportunities for the mobile health market.
Healthcare is one of the few industries that has gained more from recent innovations in technology, particularly in the field of virtual care or telemedicine.
So, if you are one who is planning to hire a custom healthcare mobile application development company, here are 11 things you should know before getting started:
#1 The unique UI/UX considerations
Just think what a clean interface on a healthcare app could do for a patient who has to enter the his/her medical records everyday or every few hours. Similarly, for a physician performing home visits, and updating every patient’s medical history after a visit will be so much easier if the app’s design is clean and easy to use.
Good UI/UX is required for every app, but with the high frequency of data input and amount of data, healthcare apps need some extra effort.
In order to develop great healthcare apps, you must consider the importance of UX Design (user experience) and UI (user interface) design.
The key is to create design that make the patient process flow as seamless as possible. If the healthcare app is patient-centric, then everything we do must have the user experience of the patient in mind.
In most of the healthcare apps, the users are vulnerable and are seeking solutions for their medical issues. So, the whole app experience shouldn’t portray anything which is negative. Be it the colors, fonts, text, etc. The UI should be personal and supportive, which strives to make people feel better and more positive.
A great UI/UX design agency can help your users excited about inputting their personal health data. Check out these screenshots of our latest healthcare app called Sternfit.
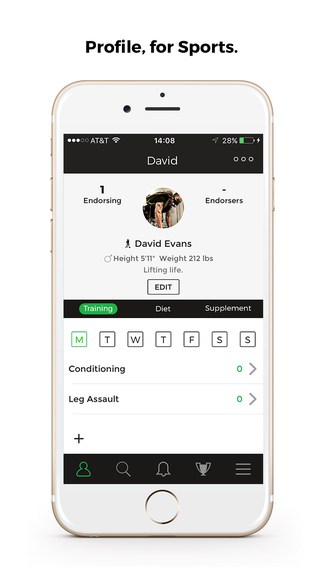
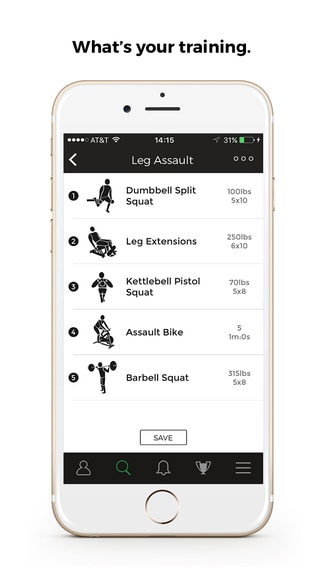
To expand the scope of what healthcare app can accomplish it is important that user is allowed to integrate other features of the phone. For example, while building the app, if you feel the app can work better if the doctor access the patient via the front camera of the phone, then allow your app to have such integration.
Jess Kadar, product manager for a collaborative care platform, says, “When designing for medical applications reduce chrome/decoration and carefully design data visualizations that create meaning and are actionable.”
He further adds, “Design clear visual designs. If you are designing for people age 40+ and/or people with chronic diseases, contrast and type hierarchy are particularly important. Focus on optimizing the signal-to-noise ratio in the UI. Get the design in the browser as early as possible and observe patients using the app.”
#2 Privacy and security of healthcare apps (read HIPAA)
Medical and healthcare apps have a lot of barriers to pass.
Since, the healthcare data is so sensitive that it can directly affect user’s safety and privacy, there are several regulations for such apps.
For example, if you are building an app for the U.S. market and your app stores or exchanges in any way with sensitive patient data, you must comply with the Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Similarly, if you are building an app for the European market, your app will come under the vigilance of EU data protection laws, such as, Data Protection Directive 1995/46/EC (Section 2.1) and the e-Privacy Directive 2002/58/EC (Section 2.2).
The Canadian government has the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) that set parameters for the administration of personal data by businesses.
So, if you plan to have a healthcare app that collects any sensitive information from users, you must include a privacy policy that explains what information is being collected and how it will be used. As the owner of a healthcare app you need to keep patients’ protected health information (PHI) a top priority.
It is not advisable to risk and breach any of these regulations, because even the app stores are very particular about the healthcare guidelines. Apple has rejected several healthcare apps in past on the basis of privacy issues.
In fact, Apple has a huge list of review guidelines for healthcare apps, and most of them are related to privacy and security of healthcare data.

#3 Testing healthcare applications
App testing is an important step in building a great app.
However, when it comes to developing healthcare apps, not testing the functionality before the release of the app can have some serious implications.
If your healthcare app failed to function properly, there is a huge risk of giving out negative or undesirable results. For instance, sensitive data pertaining to a patient’s medical history must be saved and processed accurately, failure to do so could be fatal.
Whether you opt for manual testing or test automation tools, it is important you test your healthcare app for the following:
- It’s important to test the security and authenticity for PII, PHI and other regulations such as HIPAA compliance.
- Test functional capabilities of your healthcare app, including testing of healthcare workflows.
- If you have a health app which needs geo-location services, such as fitness tracking apps, check the accuracy of those services.
- If the app interprets data from certain inputs, check the inputs in different units, from different devices, networks, and locations. It should pull correct information every time.
- Test with poor connectivity to simulate real world use cases.
- Test medical imaging apps for medical imaging.
- Test your app on different mobile platforms (iOS, Android, Windows etc.), and browsers for compatibility.
- Test your app against load and performance benchmarks.
- Usability testing is another effective technique at providing valuable insights into how a real user would use your app.
#4 Who’s Your Target Audience?
For a healthcare application, the most obvious target audience are doctors, nurses, other medical staff, pharmacists, patients, or laboratory professionals.
However, that’s not the only perspective you need to cover while developing a healthcare app.
Different people require different features, hence it’s vital to know your primary audience, followed by secondary audience, and then the tertiary (which covers a broad range of people).
Start by understanding what kind of doctors, nurses, or patients you’re developing a medical app for? For example, are you targeting only adults who use a healthcare app for tracking medication or illness? Or your motive is to help doctors or nurses during medical emergencies.
Ask yourself different questions, till you reach a point where you know whom to target, and what type of features your audience needs or problems you’re trying to solve. Here are a few pointers for your reference –
1. Will users integrate healthcare apps with wearable devices?
2. Will patients interact with each other?
3. Do patients and doctors want a face-time feature?
4. Do users want relatable and actionable information?
5. What type of platform is preferred by the target audience – iOS/Android?
Ensure that problems faced by your target audience are solved, otherwise the medical app is likely to fail.
#5 How to Plan a Budget For a Healthcare App?
On an average, the budget for creating an application varies from $10,000 to $150,000. Therefore, plan a suitable budget that covers all essential expenditures. Also, budget depends on the type of product and features installed, for example, IoT-enabled telemedicine solution or practice management application.
Every healthcare application serves a different purpose, prioritizes various features, hence requirements would be different, which affects the budget. However, considering an average budget, here’s a checklist to plan an effective budget for a healthcare application.
1. Apart from the money allocated to developing an app, set aside additional funds to cover unexpected expenses.
2. Minimum features with great functionality for users will help to stick to the planned budget.
3. Consider launching on any one platform – iOS/Android, due to time or budget constraints. If not, then a smart choice would be to launch a healthcare app on both platforms.
4. Plan budget for the future because healthcare app development doesn’t end after product delivery. It needs constant upgradation, maintenance, and improvements.
After following this checklist, the final cost of a healthcare application depends on its capabilities, functionalities, and features.
#6 HIPAA and HITECH Regulations
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) was introduced to safeguard the confidentiality of protected health information (PHI). Goal of HIPAA is to decrease healthcare abuse and fraud and to establish PHI confidentiality and security standards.
Further, HIPAA is a way for people to transfer health insurance when they lose or change jobs, and to manage health information effectively.
HIPAA violations are penalized through a four-tiered system and fines range from $100 to $50,000 per violation for each tier. Hence, while developing a healthcare application ensure that your app is HIPAA compliant.
HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) Act assures adoption of EHR at healthcare facilities. Incorporation of HITECH and HIPAA in a healthcare app ensures security and safe transfer of PHI, which is preferred by clinics and healthcare facilities.
#7 Focus on MVP Development
MVP (Minimum Viable Product) technique is the best way to start off on any project for agile development processes. Through MVP, a healthcare app has sufficient features to reach potential audiences. The final product is developed after feedback is received from users.
Consider integrating minimum features at the beginning of app development for smooth functionality, and grow once you receive feedback to create an improved version of a healthcare app.
Launching a healthcare app with a definitive MVP ensures that you stay ahead of your competition, and the fact that your app isn’t all bells and whistles shouldn’t keep you from plunging in the market.
A basic app with exceptional functionality saves time and money, which is possible through MVP. Further, MVP helps to make changes and adapt to the results, plus allowing you to test applications in real market situations.
#8 Design Scalability of Healthcare App
The first version of a healthcare app has limited functionality, and a small app is better at solving one issue effectively, thus adding value to the end-user.
Making an app scalable from the beginning is advantageous because your research about the target audience will expand over a period of time. Also, adding more features will enhance the app quality and functionality.
A scalable app assures growth with zero downtime, and doesn’t affect the experience of patients or healthcare professionals. A slow running healthcare application is a liability during medical emergencies or during remote patient monitoring. Hence, scalable apps ensure fast responses, despite the number of people using the app.
The dynamics of healthcare technology are changing rapidly, hence long-term strategies for developing a healthcare app is hardly possible. Consider scaling-up the performance of the medical app gradually as per requirements.
#9 Include Next-Generation Technologies
1. IoT (Internet of Things)
The Internet of medical things is trending in the healthcare sector for it’s usage in real-time patient monitoring, ameliorated drug management, increased patient outcome and engagement, and for better chronic care management.
IoMT devices such as sensor-enabled devices or wearables are capable of analyzing, generating, and transmitting healthcare data to the healthcare systems. Wi-Fi-enabled devices regulate machine-to-machine interaction to alleviate burden on the healthcare systems, thus reducing in-person visits and safe transfer of medical data.
2. AI and ML
Artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) in healthcare apps are consuming immense data through algorithms to perform certain tasks automatically, as this helps in remote operations and effective outcomes.
AI and ML integrated healthcare applications allow patients to have access to healthcare services at their homes 24/7. Automation helps in diagnosis and treatment of patients, thus easing workload of doctors. Here are potential applications of AI and ML in a healthcare app –
1. Image analysis in radiology
2. Research and education
3. Chatbots for real-time assistance
4. Predictive analysis
5. Precision medicine
6. Drug discovery
AI-powered healthcare apps help patients and doctors to elevate their health, manage time, and reduce medical risks of patients.
3. Blockchain
One of the major benefits of using blockchain technology in a healthcare app is to solve the issue of interoperability. This technology helps to share patient data securely, thus assuring that all records are tamper-proof.
Blockchain technology helps with the integration of several EHR systems and tracking medicine in a supply chain.
4. VR and AR
Virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) is highly used for gaming, however these technologies can be installed in healthcare apps as well.
Incorporation of VR and AR in healthcare apps helps in remote mental health therapies via simulated environment. This is a potential tool for surgeries and helps doctors treat and save lives. Further, VR and AR are changing today’s medical education and training as well.
Therefore, consider implementing these technologies according to your target audience and features.
5. Big Data
Healthcare records surplus data such as laboratory results, family medical history, allergies, operations, major or minor diseases, immunizations, and more in the form of big data. AI algorithms and IoT processes this data to give an output in the form of diagnosis or treatment.
Data helps in automation, image analysis, preventive measures, and predictive analysis. This is a tool for drug discovery as data analyzes potential combinations for creating an effective drug against a disease.
#10 Consider APIs and Integrations
To attract users, integrate healthcare apps with features and services such as chats and calling, face-time, e-prescriptions, or a chatbot.
Also, ensure that the corresponding APIs (Application Programming Interface) is available for commercial usage. APIs develops a connection between additional services and the app for improved functionality.
APIs are designed to support payment processes, data collection, and communication between physicians and patients.
#11 Test Your Healthcare Application
Testing your healthcare application from the start helps to spot developmental and user experience issues instantly, and repair them.
Testing a healthcare app helps to dive deep into your target group’s expectations and their way of thinking. This helps you to redesign features and services with more accuracy and prominence.
In the end, design a healthcare application that works for your potential consumers.
